EDUCATION
About Diamond Certificates
Diamond education / certification. The two biggest laboratories in the world are GIA and EGL. Both of these are reputable with the main difference being that GIA applies a stricter grading system. Whereas the EGL approach is ‘softer’.
This may result in the same stone obtaining a different grading from the two laboratories. GIA might grade the colour of a stone as ‘H’ while EGL might grade it as ‘F/G’. Consequently, GIA might grade the clarity of a stone as ‘SI2’ while EGL might grade it as ‘VS2/SI1’.
Stone Grading
Both these laboratories grade stones according to their own master set of colour stones and clarity rules. This difference is also reflected in the price of the stone. A stone with a softer grading will carry a bigger discount than a stone with a stricter grading. Therefore, it equals out the playing field.
Grades Of Colour / Diamond Education
EGL and GIA grades colour according to the international scale of D to Z. Every letter on the scale represents a range of tone and saturation.
Two diamonds belonging to the same colour range can actually differ in their depth of colour. Since brightness and fire, which are the result of good proportions, can affect a diamond’s colour. It is important to grade a diamond not only face down but also face up. Usually as diamonds are typically set and worn face up.
In the face up position, diamonds with moderate or distinct fluorescence have a better colour than less fluorescent ones.
Colour and Clarity
Colour and clarity grading is an opinion of humans grading the stones and not an exact science. The same lab might at different times (with different employees) grade the same stone differently.
However, on the most important part of the grading report, both laboratories are exactly the same. The proportions of the diamond i.e. the table width, total depth, crown and pavilion angles etc. These are an exact science and are measured and calculated using sophisticated measuring instruments.
These proportions of the diamond determine the brilliance of the stone and therefore should be ideal. An ideal cut ‘H’ is a much better stone to buy than a poorly cut ‘F’.
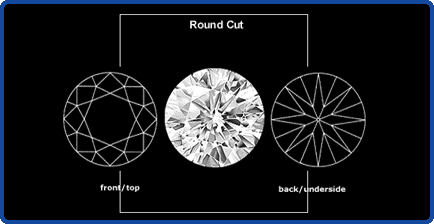
This is the most common style of cutting both diamonds and coloured stones.
The standard round brilliant consists of 57 facets; 1 table, 8 bezel facets, 8 star facets, 16 upper-girdle facets on the crown; 8 pavilion facets, 16 lower girdle facets; and usually a culet on the pavilion.
Modifications of the round brilliant include such fancy shapes as the marquise, half moon, pear shape and many others.
What determines the value of a diamond?
There are four main factors that determine the value of a diamond. They are referred to as the Four C’s:
- Carat Weight (size)
- Cut
- Colour
- Clarity
The Four C's
Carat
Carat refers to the weight of a diamond. Each carat is subdivided into 100 points, allowing
for precise measurements. For instance, a diamond weighing 50 points is recognized as a
half-carat or 0.50-carat. The carat weight of a diamond is a significant indicator of its size
and plays a crucial role in determining the gem's value, with pricing typically reflecting this
key characteristic.
Cut
The cut of a diamond is all about its proportions, symmetry, and polish. This factor
determines how well the diamond interacts with light, influencing its brilliance, fire, and
scintillation. Cuts are graded from Excellent to Poor and directly affect the diamond's beauty
and value. A well-cut diamond will appear luminous and vibrant, expertly crafted to enhance
its natural sparkle.
Colour
Colour in diamonds ranges from colourless to light yellow or brown, graded on a scale from
D (colourless) to Z (light colour). The less colour a diamond has, the higher its grade and
value, as colourless diamonds allow more light to pass through, resulting in greater sparkle.
Clarity
Clarity refers to the presence of internal characteristics called inclusions and surface
defects known as blemishes. Clarity is graded from Flawless to Included, based on the
visibility of these characteristics. While high-clarity diamonds are more prized, many
inclusions and blemishes are not visible to the naked eye, allowing for a range of options.
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the glow a diamond emits when exposed to ultraviolet light. This characteristic is graded from None to Very Strong. While some diamonds show noticeable
fluorescence, it does not usually affect the stone's overall appearance in normal lighting
conditions. In some instances, fluorescence can even make a diamond with a slight yellow
hue appear more colourless.
